Posterior (or dorsal) means the opposite of anterior "back of" or "behind/on the back" This is easy to remember because "posterior" is another word for your rear end, which is on your backside An anatomy test question might ask, "Your sternum is _____ to your spine" The internal jugular veins collect blood from the brain as well as the superficial structures of the head and neck before descending through the neck towards the heart Innerbody Research is the largest home health and wellness guide online, helping over one million visitors each month learn about health products and servicesAnatomy of the Head It may seem unusual to discuss anatomy in haircuts, but knowing the references used for the areas of the head and what they specifically indicate help you to understand what is intended with a particular haircut The following are the terms for the basic features of the head as they affect haircutting

Head Definition Anatomy Britannica
Back side of head anatomy
Back side of head anatomy-A chicken's head has several parts, as shown in Figure 7 One of the most prominent features on a chicken's head is the comb Figure 8 shows different types of combs A chicken's comb and wattles are red, soft, and warm Chickens do not have external ears as humans do The ears are just openings into the ear canal, and each is protectedCraniotomy A surgeon drills a hole into the side of the skull to relieve high pressures Lumbar drain A drain is placed into the fluid around the spinal cord This can relieve pressure on the




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
Low back pain is a very common complaint for a simple reason Since the lumbar spine is connected to your pelvis, this is where most of your weight bearing and body movement takes place Typically, this is where people tend to place too much pressure, such as lifting up a heavy box, twisting to move a heavy load, or carrying a heavy object 171,391 human head anatomy stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See human head anatomy stock video clips of 1,714 womans chest men body icon medical physiology nasal model human part female body icons body parts line art lips line anatomy of nose tongue in mouth profile Try these curated collectionsHead hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such an
These headaches occur in the back and right side of the head They may include a tightness of the neck or scalp They feel like a dull, tight constricting pain that isn't throbbingOccipital neuralgia is a distinct type of headache characterized by piercing, throbbing, or electricshocklike chronic pain in the upper neck, back of the head, and behind the ears, usually on one side of the head Typically, the pain of occipital neuralgia begins in the neck and then spreads upwards Some individuals will also experience pain in the scalp, forehead, and behind the eyesExtending from underneath the chin, to the posterior aspect of the head They ultimately drain into the deep lymph nodes Occipital There are usually between 13 occipital lymph nodes
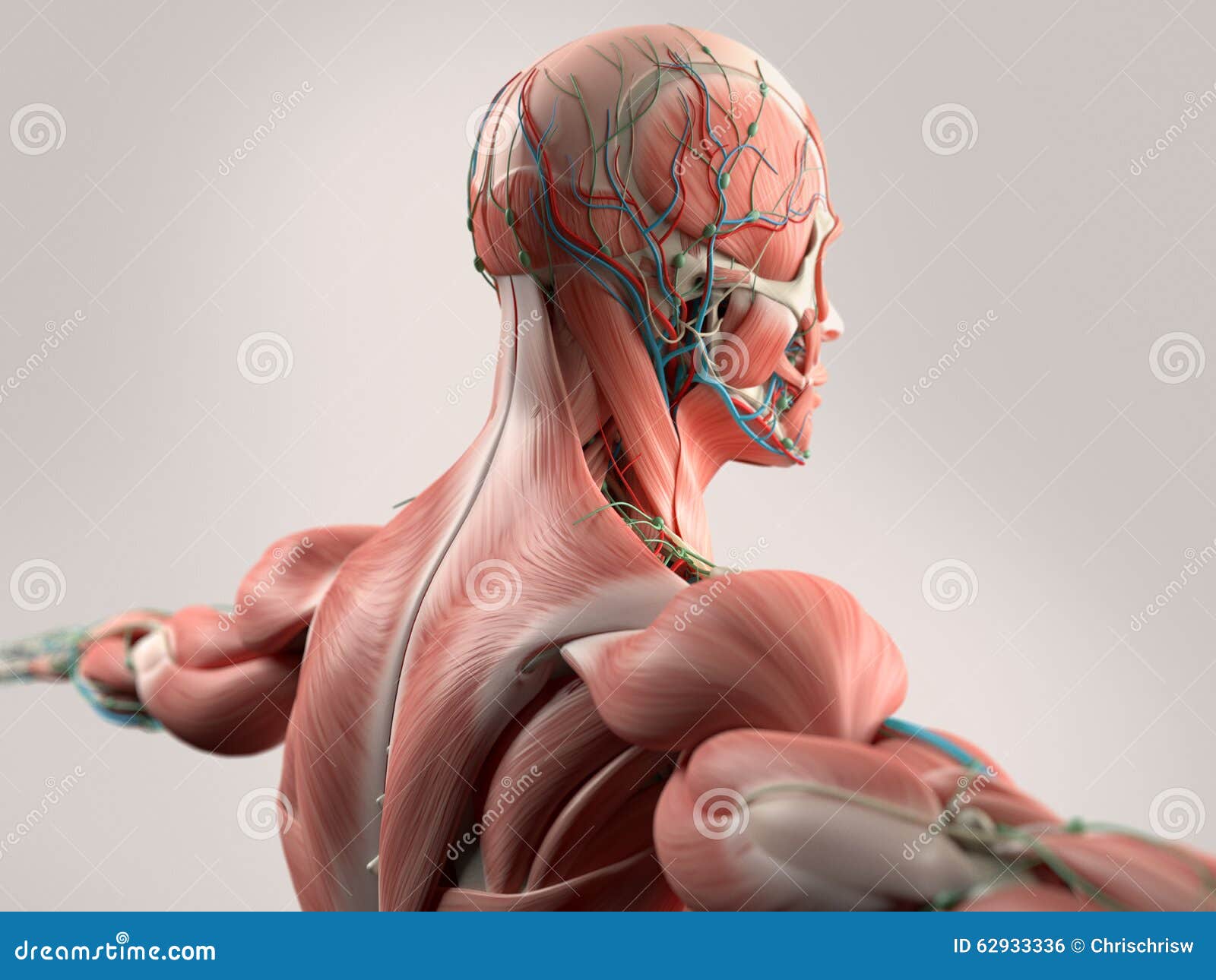
Anatomical Directional Terms Anterior In front of, front Posterior After, behind, following, toward the rear Distal Away from, farther from the origin Proximal Near, closer to the origin Dorsal Near the upper surface, toward the back Ventral Toward the bottom, toward the belly Superior Above, over Inferior Below, under Lateral Toward the side, away from the midFemale doctor teaching using anatomical model human anatomy organs back view stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images human skeleton ,upper part back side human anatomy organs back view stock illustrations human heart (front, back, section) human anatomy organs back view stock illustrations The nerves of the head and neck include the most vital and important organs of the nervous system — the brain and spinal cord — as well as the organs of the special senses In addition, in this region we also find the major cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system to the organs, skin, and muscles of the head and neck
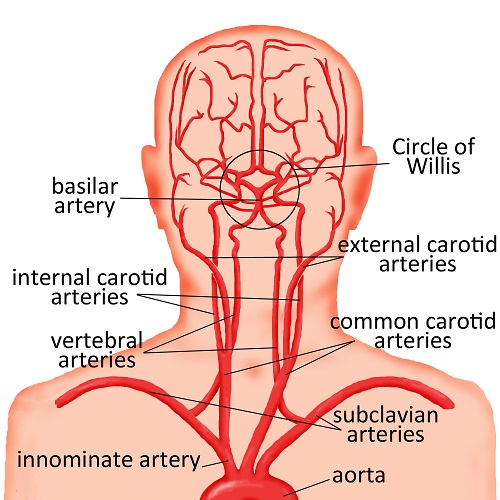



Abnormalities Of The Head And Neck Arteries Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Children S Wisconsin



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
13,276 anatomy of the head and neck stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See anatomy of the head and neck stock video clips of 133 muscle head anatomy vocal organ diagram female neck anatomy neck wireframe head neck human anatomy head artery anatomy face pharynx vector neck degree head anatomy 3dAbs=anterior side The word ventral literally means belly!Type 1 bony spur along lateral side of MT head (blue arrow)Type 2 lateral bowing of the 5th MT shaft with a normal intermetatarsal angle between 4 thand 5 MT (normal range is between 65 –8 degrees)Type 3 lateral deviation of the 5th MT (opposite appearance of the 1st MT head in hallux valgus) with increased angle between 4 thand 5 MT




Human Body Anatomy Of A Man Muscles Structure Of A Male Front View Side View And Perspective 3d Render Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub
Head, in human anatomy, the upper portion of the body, consisting of the skull with its coverings and contents, including the lower jaw It is attached to the spinal column by way of the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, and connected with the trunk of the body by the muscles, blood vessels, and nerves that constitute the neckBack Of Ear Anatomy Earlobe Anatomy Function And Treatment ImgLewis Essential to human hearing and balance, the ears are located on either side of the head Learn about the organs and body parts The inner ear, which controls hearing and balance, is made up of three main parts—the cochlea, vestibule, and the semicircular canals The front side ("heads") of a coin Reverse The back side ("tails") of a coin Edge The outer border of a coin Edges can be plain, reeded, lettered, or decorated Rim The raised part of the edge on both sides of a coin that helps protect the coin's design from wear Legend The principal inscription or lettering on a coin Mint Mark




Occipital Neuralgia Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment



Human Head Wikipedia
The back has different muscle groups that work together to allow movement There are groups of muscles that move the Head Shoulders Upper arms Spine (vertebral column) Upper leg (thigh) Other muscles beyond the back also help move the head, shoulders, arms, and legs For example, some muscles located in the chest also help move the shouldersDermatomes of the head, face, and neck There are 31 segments of the spinal cord, each with a pair (right and left) of ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots that innervate motor and sensory function, respectively The anterior and posterior nerve roots combine on Below we have mentioned few specific symptoms that may cause Pain in back of head at base of skull and neck and shoulder Occipital neuralgia can cause sudden, severe, intense pain that feels like a piercing, stabbing, electric shock in the back of the head and neck Pain in the head either one side or both side




Nerves Of The Head And Neck Interactive Anatomy Guide




The Skull Anatomy And Physiology
Neck Anatomy Muscles Pictures There are many muscles around the neck that help to support the cervical spine and allow you to move your head in different directions Here is a list of the many muscles that exist in the neck Longus Colli & Capitis – Responsible for flexion of the head and neck Rectus Capitis Anterior – Responsible forBack anatomy Bones, nerves, and conditions The cervical spine protects the nerves connecting to the brain, allowing the head to move freely while supporting its weightPoor posture If you tend to slouch when you sit or stand, that can strain the muscles in the back of your head, upper back, neck, and jaw It also can put pressure on the nerves in those areas
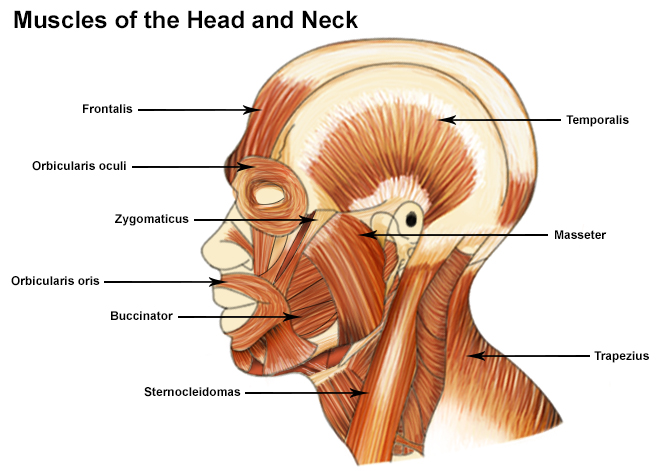



Seer Training Muscles Of The Head And Neck




Skull Back View Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
The occipital glands (lymphoglandulæ occipitales), one to three in nu ber, are placed on the back of the head close to the margin of the Trapezius and resting on the insertion of the Semispinalis capitisTheir afferent vessels drain the occipital region of the scalp, while their efferents pass to the superior deep cervical glands The posterior auricular glands (lymphoglandulæ auriculares Back anatomy The back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions It comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles;The cervical spine supports the weight and movement of your head and protects the nerves exiting your brain The lumbar spine – the lower back, composed of five vertebrae, provides support for the majority of your body's weight The thoracic spine – the middle back, made up of the 12 vertebrae in between the cervical and lumbar spine
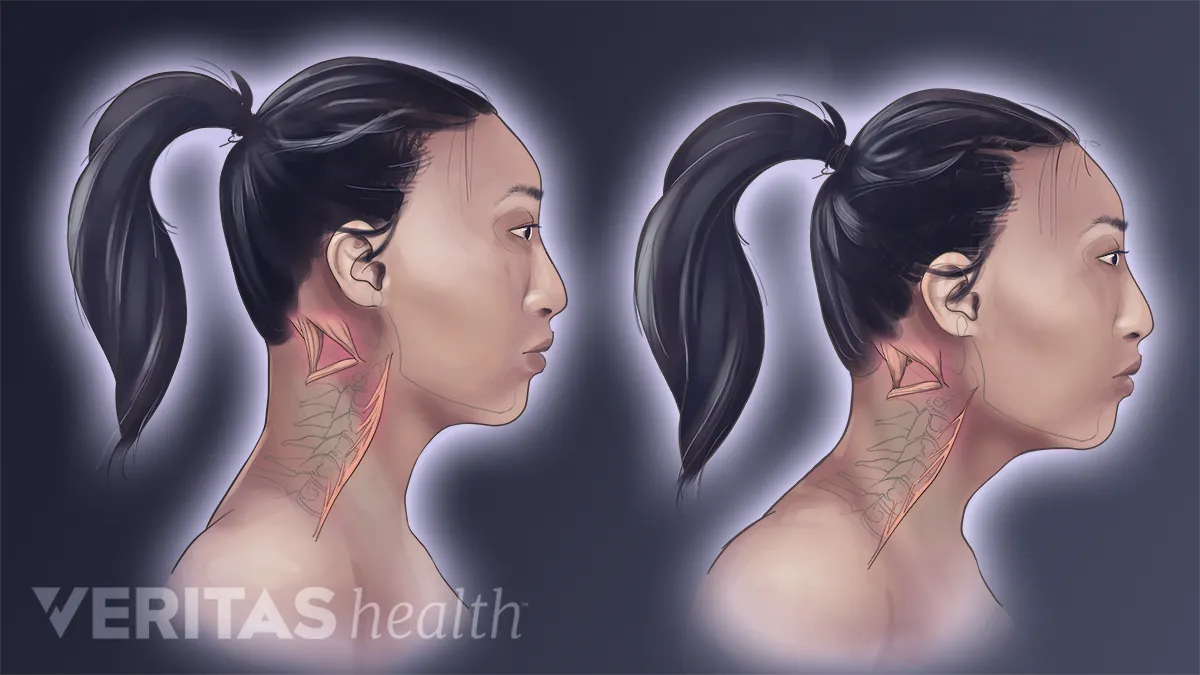



Forward Head Posture S Effect On Neck Muscles
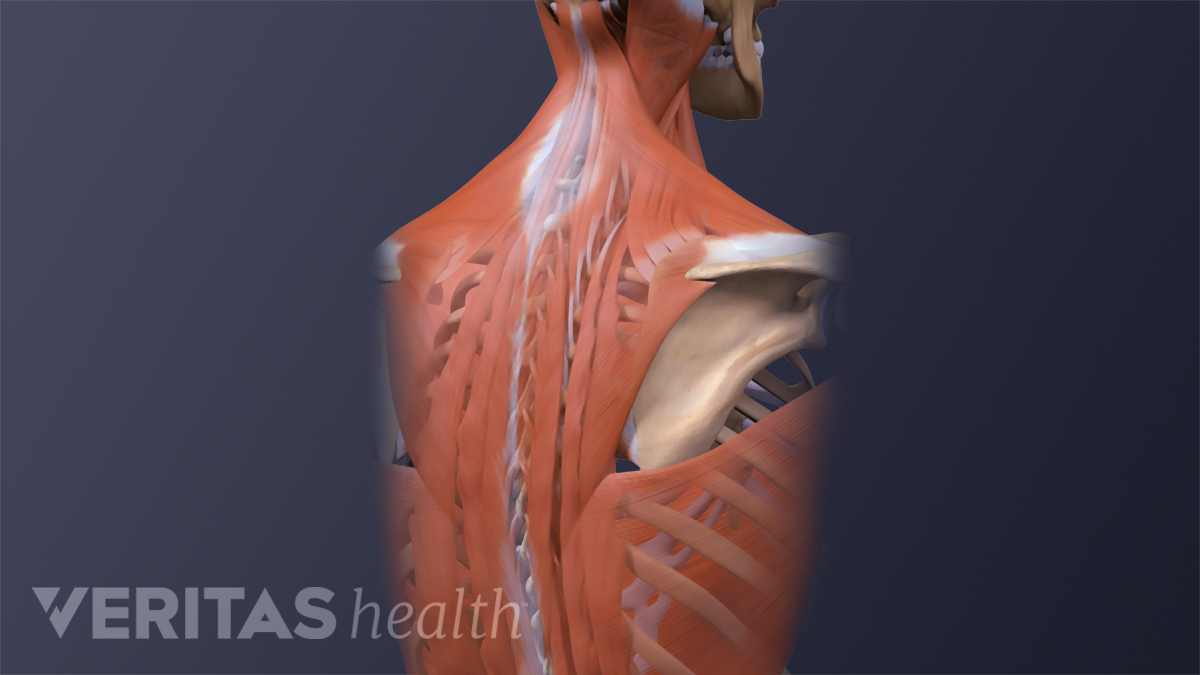



Causes Of Upper Back Pain
New users enjoy 60% OFF 172,564,554 stock photos online In addition to housing main parts of the nervous system — the brain and spine — and the start of the digestive system, the head contains many important sensory organsDownload 185 Man Body Anatomy Front Back Side Stock Illustrations, Vectors & Clipart for FREE or amazingly low rates!




Pin On Massage Board
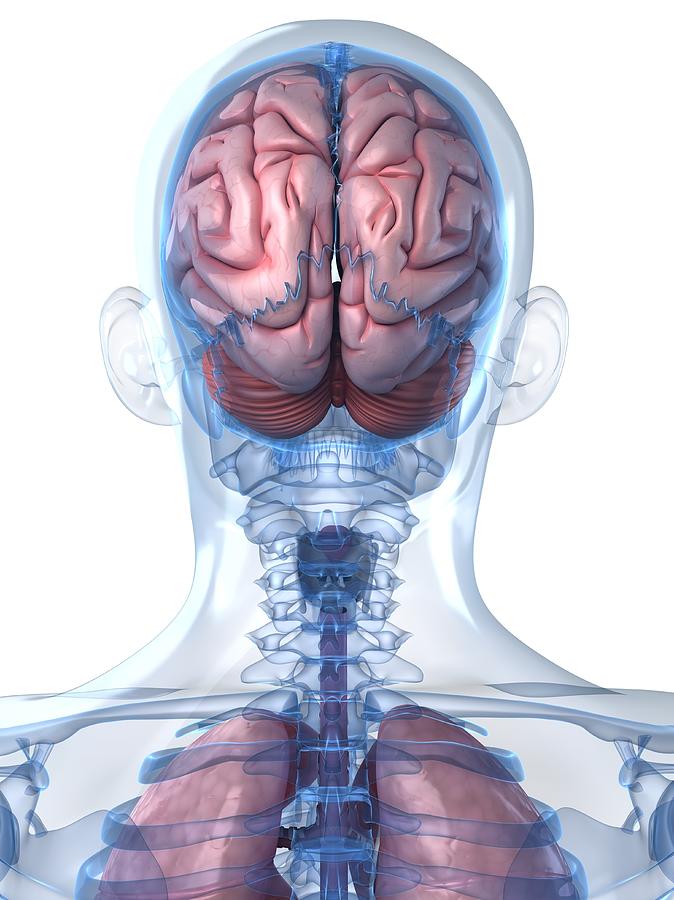



Head Anatomy Artwork By Sciepro
Human Head Back Side Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View from ipinimgcom It descends between the median line and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus, and, at the lower part of the neck, passes beneath that muscle to open into Anatomists tend to classify the body into during muscle traction, the cheeks are pulled The external jugular veins descend on either side of the neck, passing over the sternomastoid muscles and beneath the platysma They empty into the right and left subclavian veins in the base of the neck The internal jugular veins form the major venous drainage of the head and neck and are deep veins that parallel the common carotid arteryThe talus is generally thought of as having three parts the body, the head, and the neck (Figure 5) The talar body, which is roughly square in shape and is topped by the dome, connects the talus to the lower leg at the ankle joint The talar head is adjacent to the navicular bone to form the talonavicular joint The talar neck is located




Backside Anatomy Images Life Drawing Human Body Anatomy




Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing
Muscles of the Head and Neck Humans have welldeveloped muscles in the face that permit a large variety of facial expressions Because the muscles are used to show surprise, disgust, anger, fear, and other emotions, they are an important means of nonverbal communication Muscles of facial expression include frontalis, orbicularis oris, larisExtrinsic and intrinsic The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbsThe Anatomy of the Elbow The elbow is a hinged joint made up of three bones, the humerus, ulna, and radius The ends of the bones are covered with cartilage Cartilage has a rubbery consistency that allows the joints to slide easily against one another and absorb shock The bones are held together with ligaments that form the joint capsule
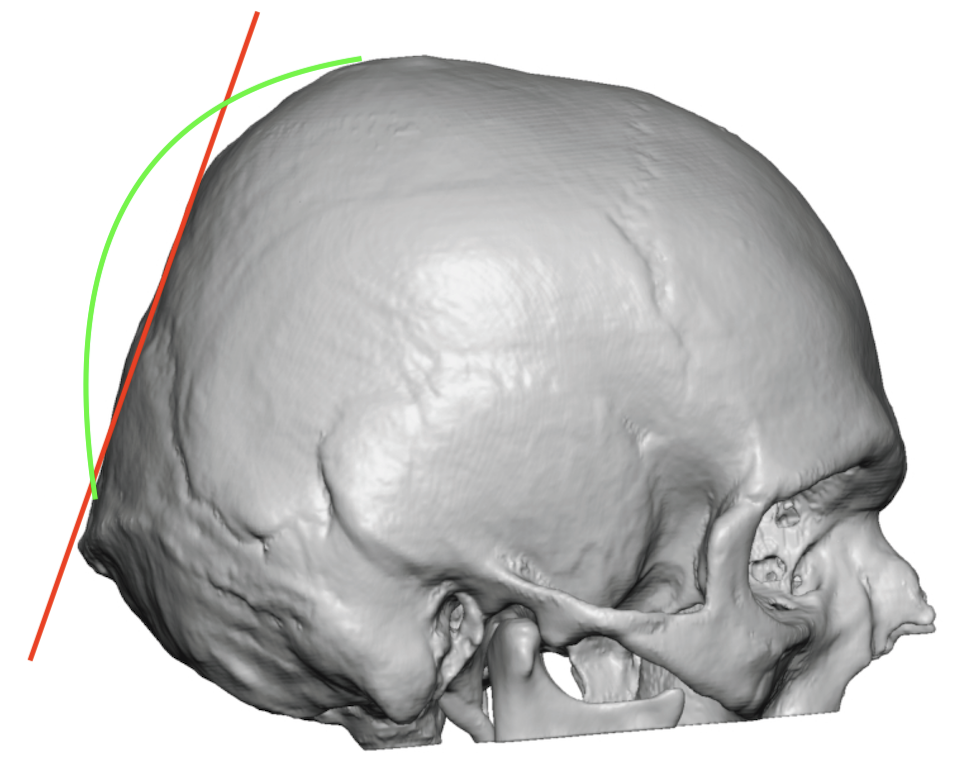



Natural Vs Desired Male Back Of Head Shape Ct Scan Side View Dr Barry Eppley Indianapolis Copy Explore Plastic Surgery




Back Of Head Anatomy Muscles Manual
Splenius capitis Located in the back of the neck, it helps the erection of the head as well as extension, sidetoside movement, and rotation of the head and neck to one side Longissimus capitis It allows rotation reflex of head to one side, and is part of the intermediate column of the muscle group sacrospinalis that runs along the neck and The superficial lymph nodes of the head and neck receive lymph from the scalp, face and neck They are arranged in a ring shape;The occipital bone is the trapezoidshaped bone at the lowerback of the cranium (skull) The occipital bone houses the back part of the brain and is one of seven bones that come together to form the skull It is located next to five of the cranium bones As a person ages, their occipital bones will fuse to the other bones of their skull




Head Definition Anatomy Britannica



Side Back Human Skull Stock Illustrations 164 Side Back Human Skull Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
These two terms, used in anatomy and embryology, describe something at the back (dorsal) or front/belly (ventral) of an organism The dorsal (from Latin dorsum 'back') surface of an organism refers to the back, or upper side, of an organism If talking about The head and neck receives the majority of its blood supply through the carotid and vertebral arteries This article shall explore the anatomy of this arterial system – its anatomical course, branches, and clinical correlations The pain in the back of your head occurs when one or a combination of factors affect your brain The Mayo Clinic says that these factors can be chemical activity in your brain, the nerves of blood vessels surrounding your skull, or the muscles at the back of the head and neck 1 Also, some people are more prone to headaches than others Knowing what causes headaches




Male Anatomy Of Head Neck And Back With Musculature Computer Illustration Normal Transparent Stock Photo




Standard Anatomical Position An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The neck refers to the collection of structures that connect the head to the torso It is a complex structure composed of many bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other connective tissues The cervical spine is the bony part of the neck Its primary function is to provide support for the skull, while still allowing for movement It is the most flexible part of the




3d Illustration Female Head Muscles Anatomy Stock Illustration




Anatomy Head Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14150/Neck_muscles.png)



Neck Muscles Anatomy List Origins Insertions Action Kenhub




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
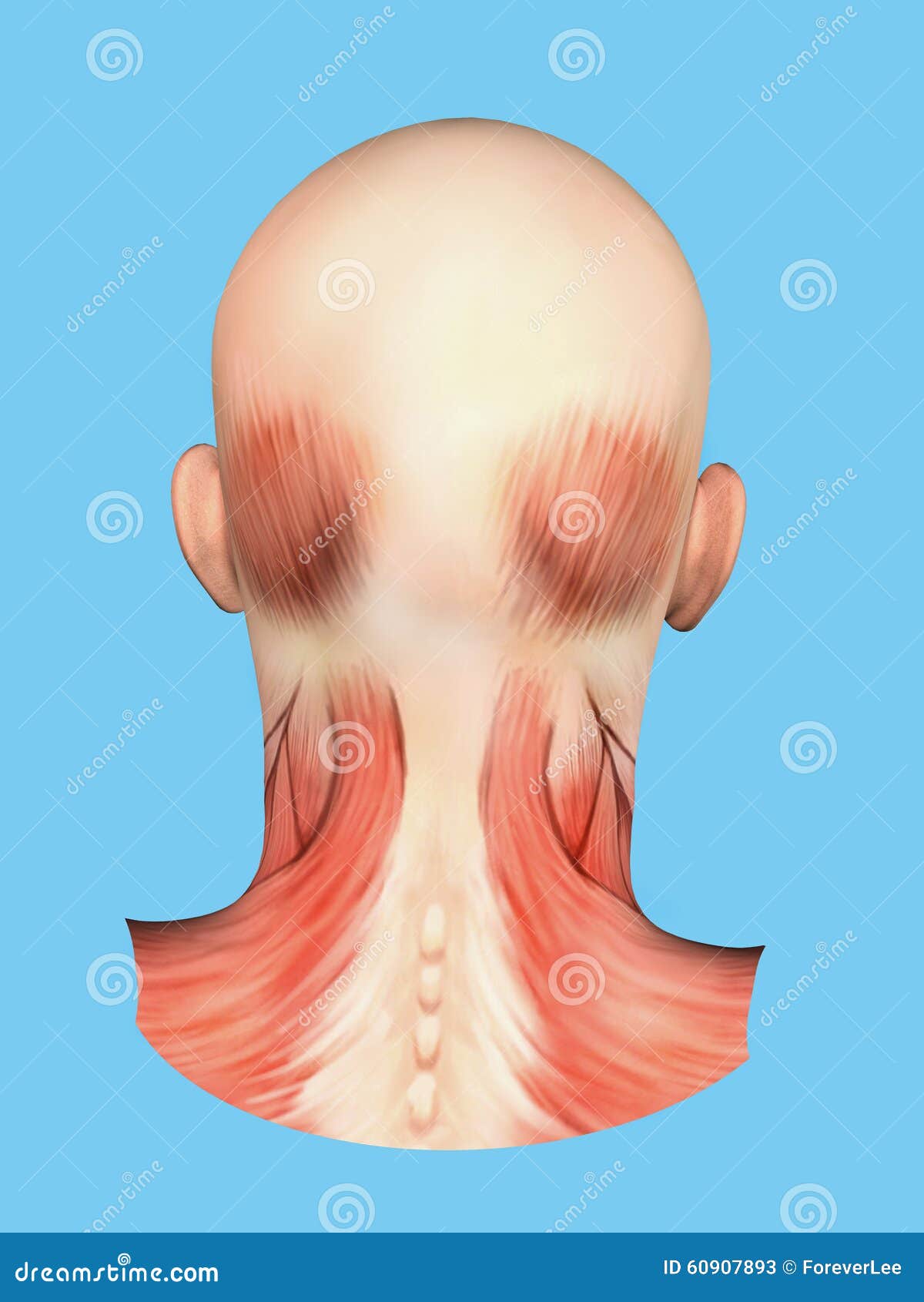



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck




Human Skull Back View Very Detailed And Scientifically Correct Human Skull Back View On White Background Anatomy Image Canstock



1
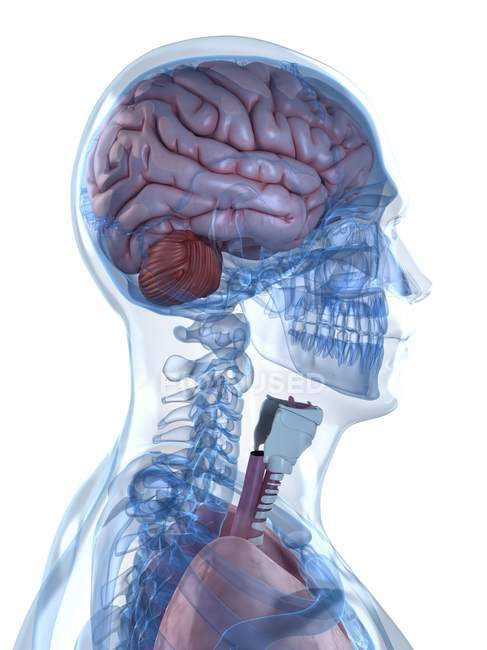



Skeletal System And Brain Structure Human Anatomy Background Stock Photo




Back Female Head Anatomy Canstock




Xray Of Human Head Showing Neck Contortion Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Man Body Model Front Back And Side Human Poses Male Human Silhouette Anatomy Stock Vector Vector And Low Budget Royalty Free Image Pic Esy Agefotostock




Illustration Of A Human Head Bones Types Side Front And Back View Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Common Causes And Treatments For Back Pain And Neck Pain Health File Telugu News Tv5 News Youtube




Foramen Magnum Anatomy Britannica
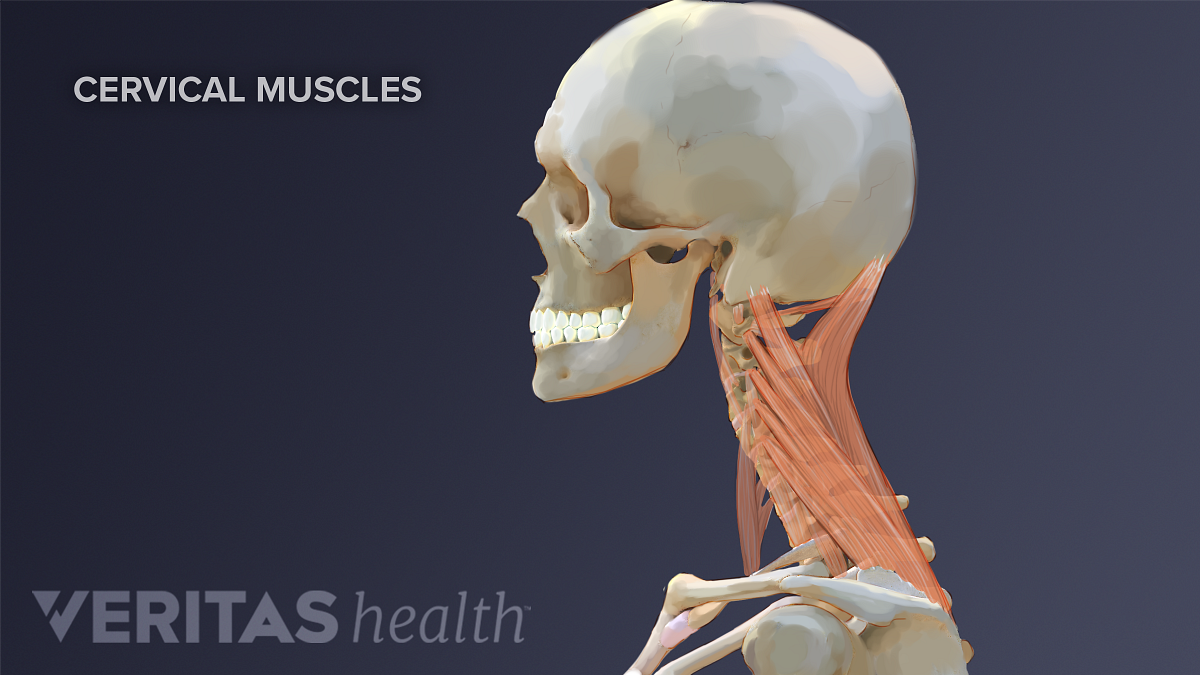



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues




Human Anatomy Side View Of Head On Dark Background Stock Illustration Illustration Of Veins Background




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley




Cervical Spine Anatomy Neck




Human Head Back Side Human Anatomy Back Of Head Anatomy Back Of Head Human Anatomy Head Anatomy Head Muscles Human Skull Anatomy




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/mandibula-2/6BJoakCePH6hpiuPRM237g_Mandible_02.png)



Skull Anatomy Anterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Kenhub



Why Can I Feel Two Large Bumps In My Skull On The Right And Left Side Of The Back Of My Head Quora




Side View Of Nervous System Of Head Skeleton Stock Illustration Illustration Of Biology Clipart
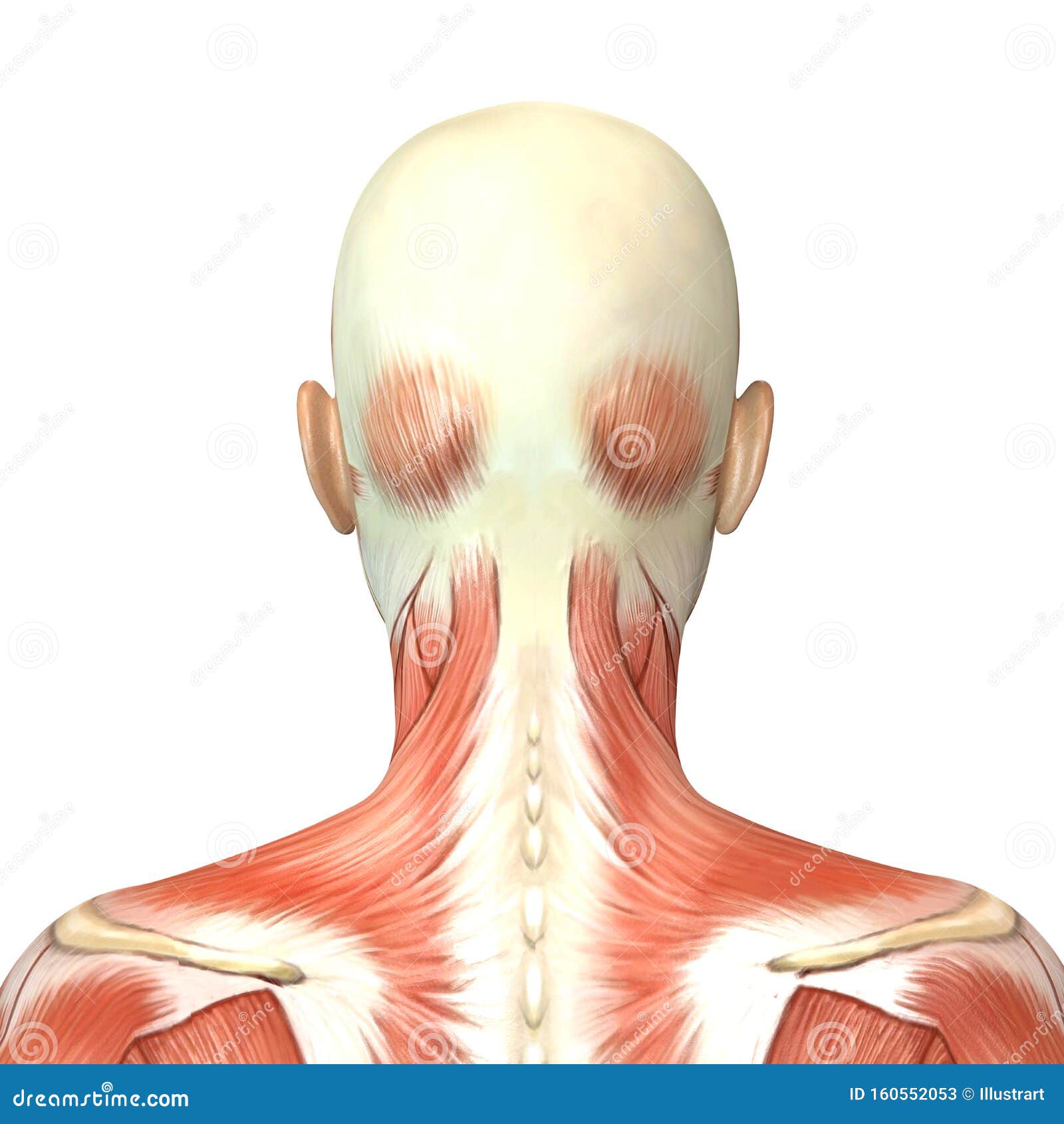



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Spine Structure Function Parts Segments Spine Problems Spine Health
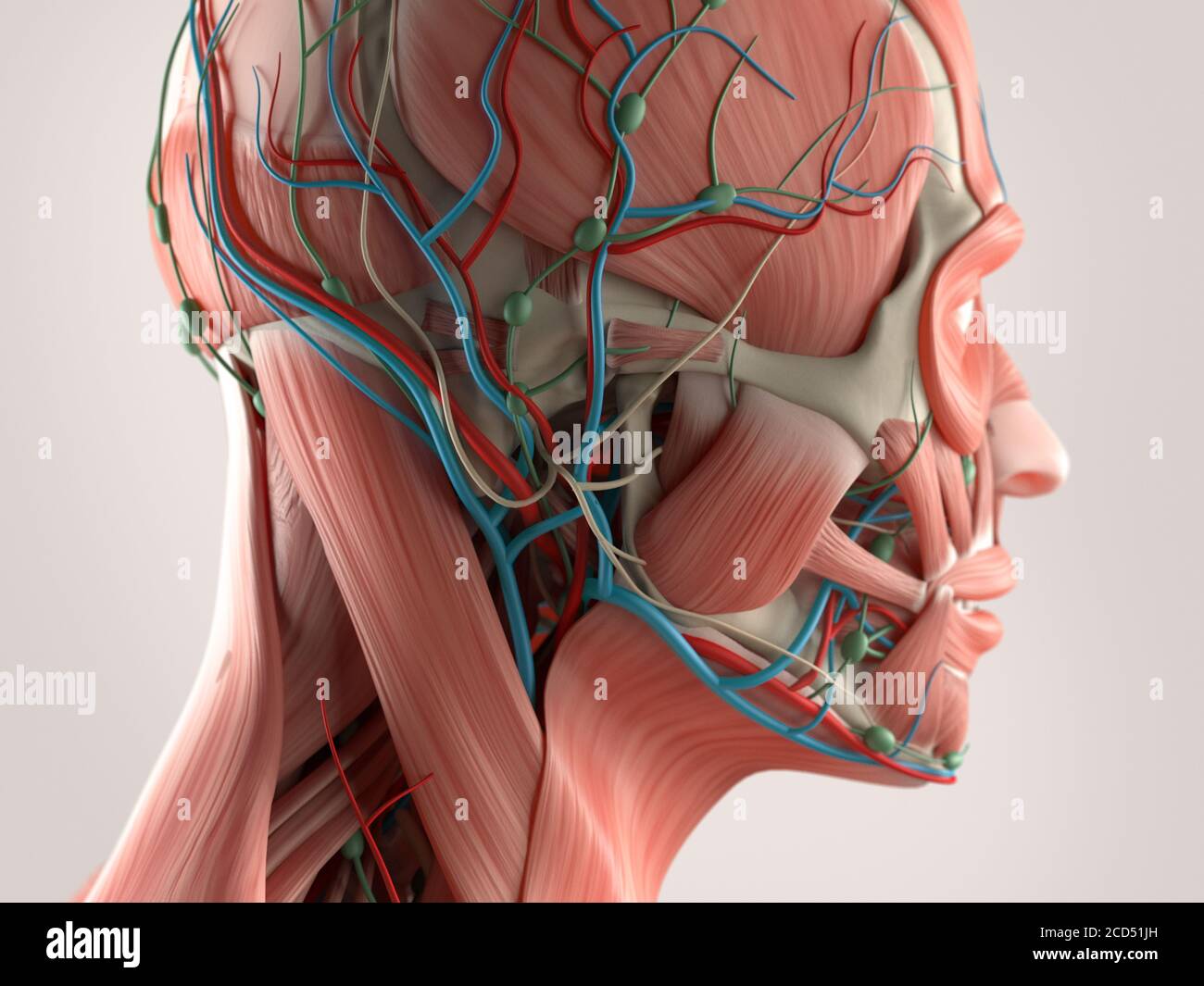



Human Head Bone And Muscle High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I




Illustration Of Male Head And Chest Anatomy Stock Photo Alamy




Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing




Human Head Wikipedia
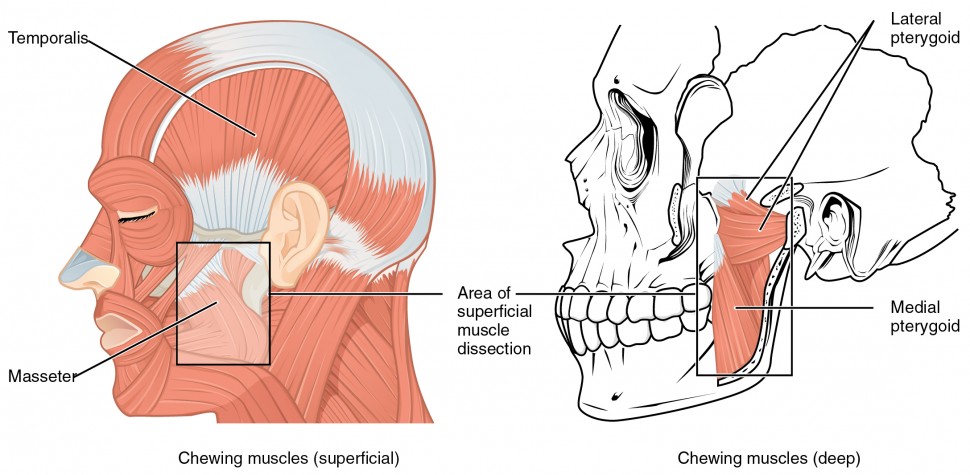



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/temporal-branches-of-facial-nerve/RzcTv6r5o1xj8GRxxGMnQ_Rr._temporales_nervi_facialis_02.png)



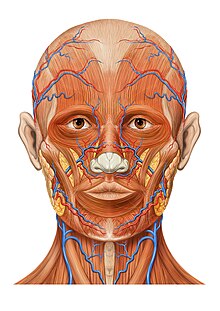
Superficial Nerves Of The Face And Scalp Anatomy Kenhub




Human Head Backside Anatomy Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile




Human Anatomy Of Side Of Head Backlit On Dark Background Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Depositphotos_19871399_original-56a05f523df78cafdaa14cd1.jpg)



Hamstring Muscles And Your Back Pain




Crown Of Head Conditions Injuries And More



1




Upper Cervical Spine Disorders Anatomy Of The Head And Upper Neck
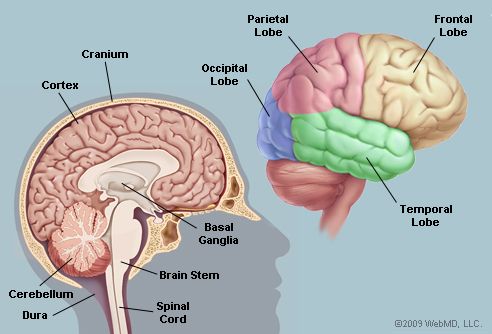



Brain Human Anatomy Picture Function Parts Conditions And More
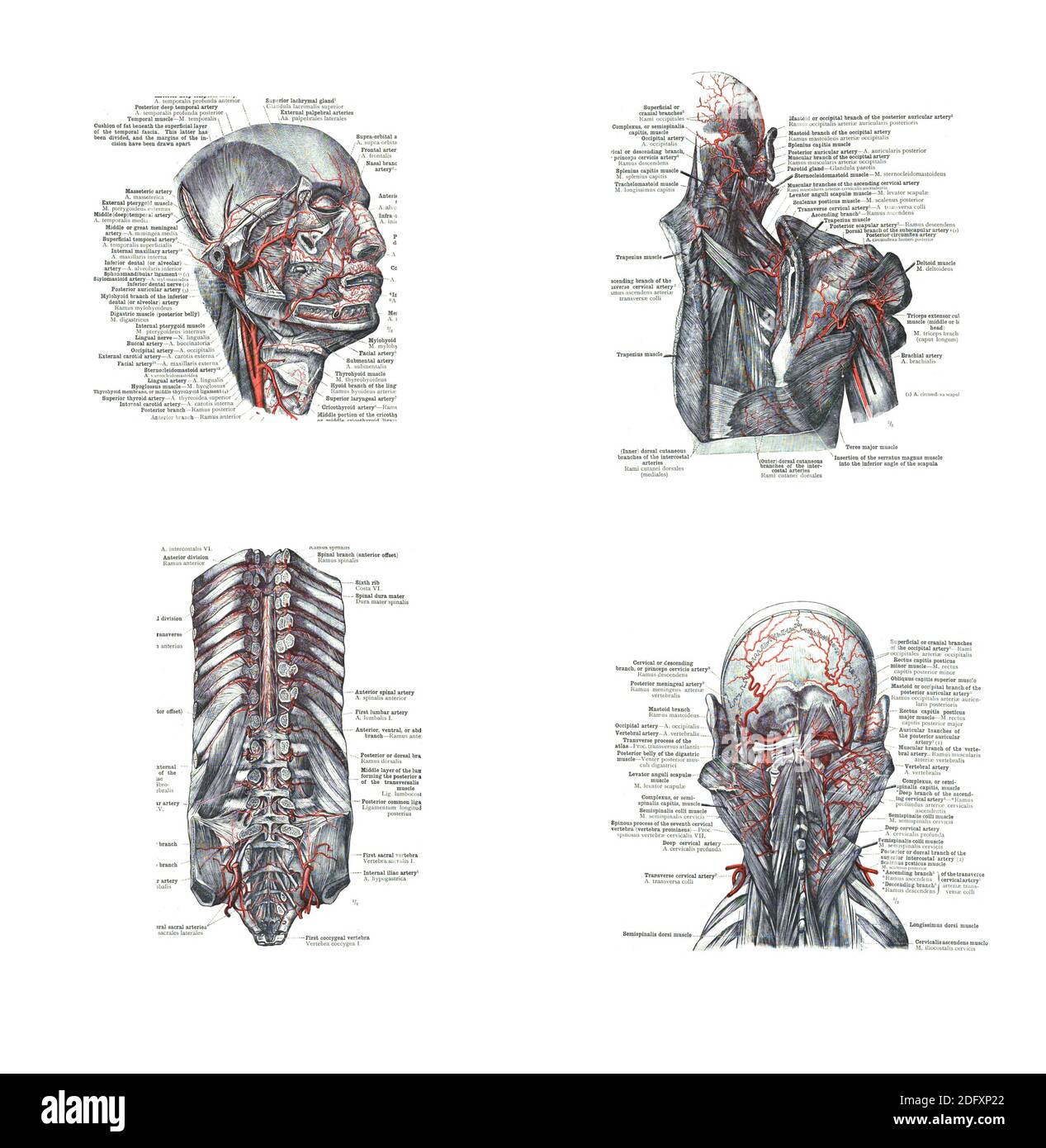



4 Views Of The Head Back And Spine From An Atlas Of Human Anatomy Carl Toldt 1904 Stock Photo Alamy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/posterior-and-lateral-views-of-the-skull/U0Gu2npm5ZRSP1eZgc4Jbw_Posterior_view_of_skull.png)



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub



1




Head Circulatory And Nervous System Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
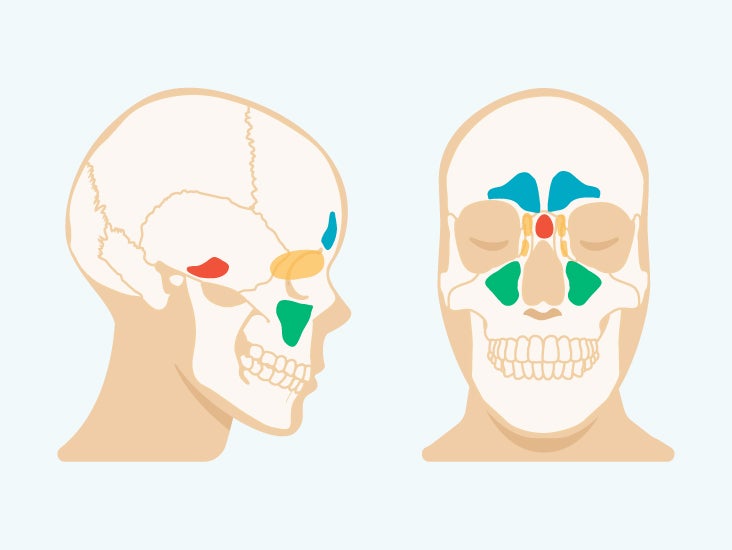



Sinus Cavities In The Head Anatomy Diagram Pictures




Back Of The Head Anatomy Anatomy Drawing Diagram




Anatomy Of Vein On Back Head Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile




Human Skull 3 4 Back View Skull Reference Human Skull Skull Anatomy




Brain Structure And Function




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
/GettyImages-530290688-6fd15665d8b644d49e78ee6844675a36.jpg)



External Jugular Vein Anatomy Function And Significance
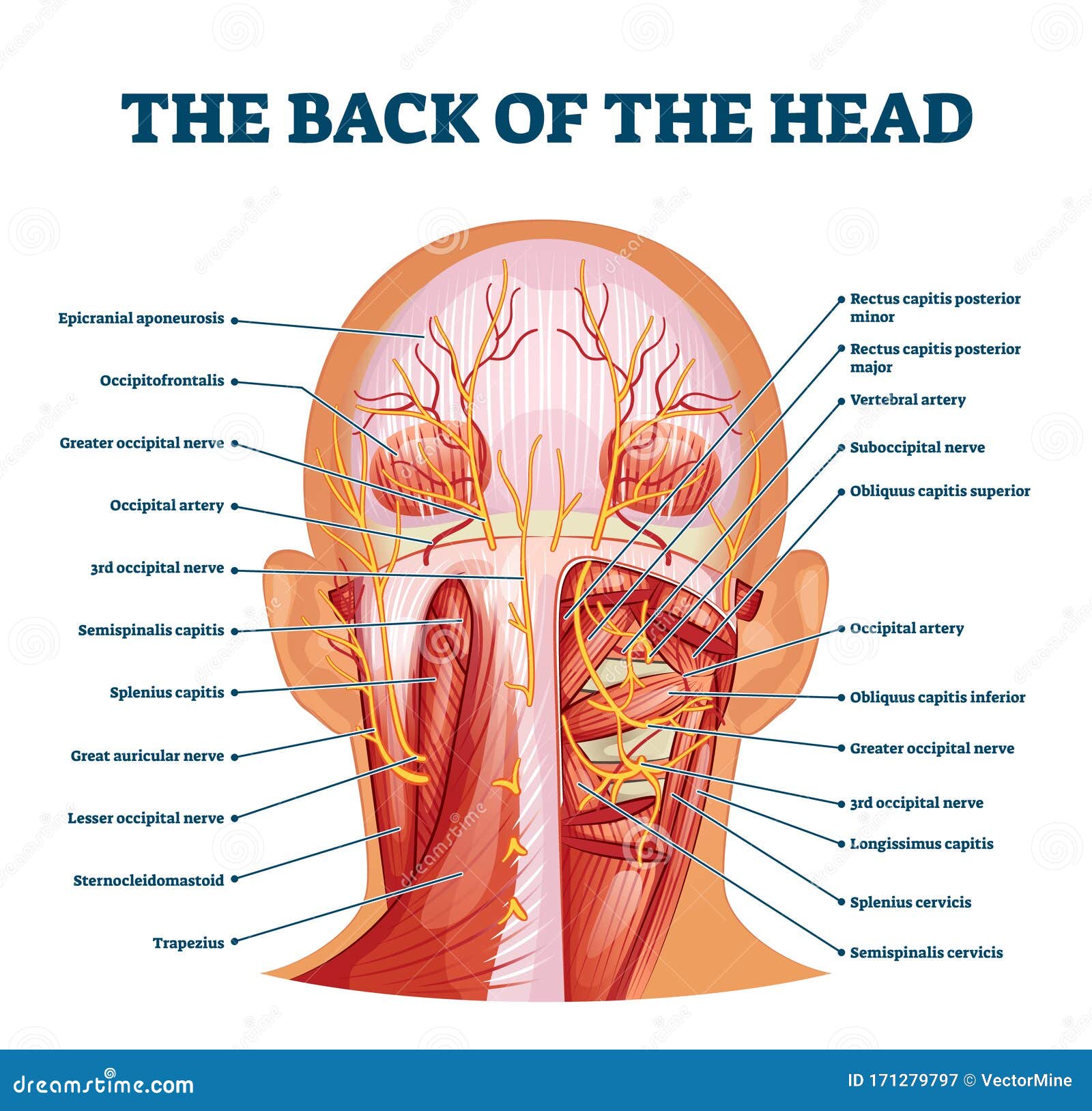



Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle




Occipital Bone Wikipedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9490/skull-posterior-lateral-views_english.jpg)



Posterior And Lateral Views Of The Skull Anatomy Kenhub



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
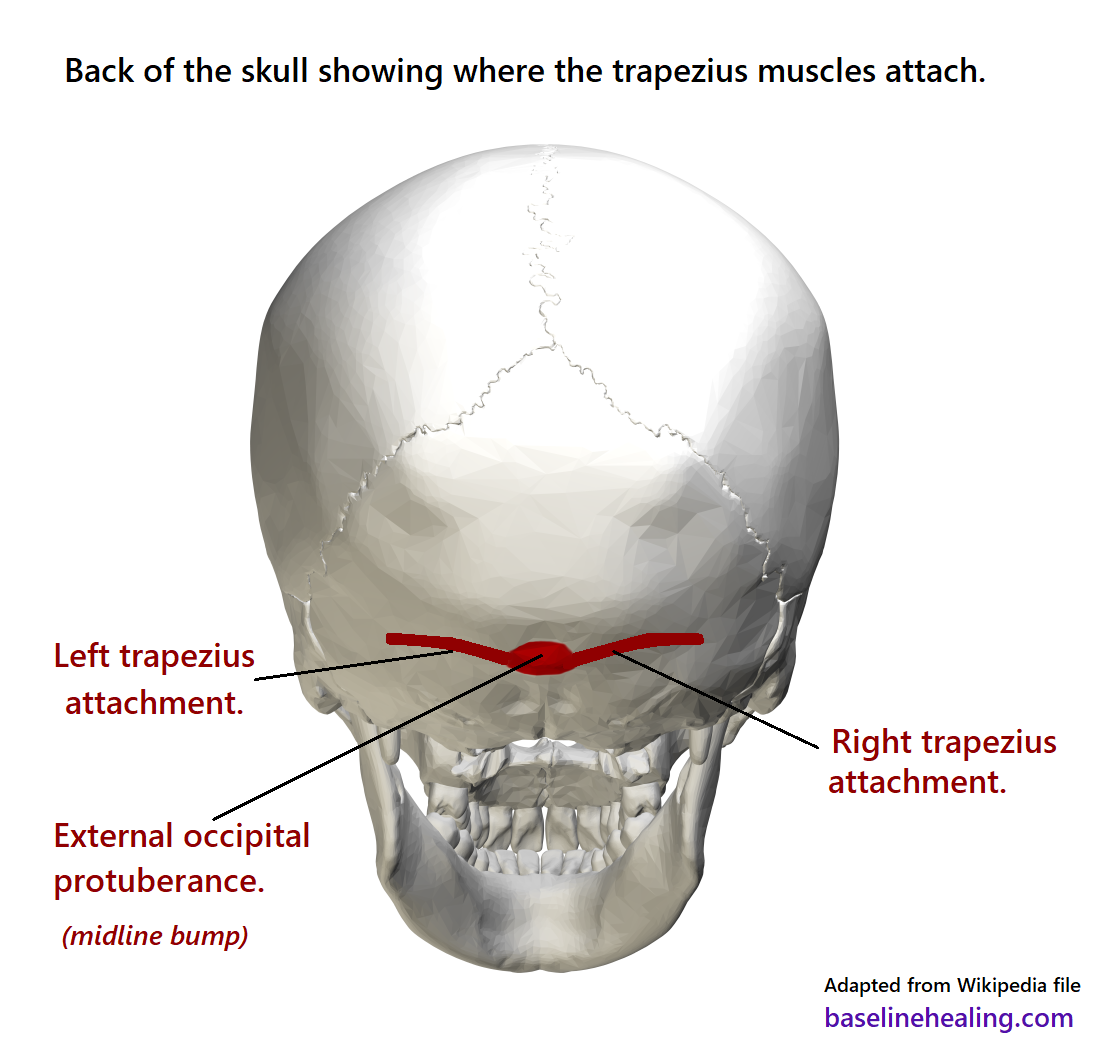



Upper Body To Base Line Connection The Trapezius Muscles




The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I




Human Head Backside Anatomy Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile
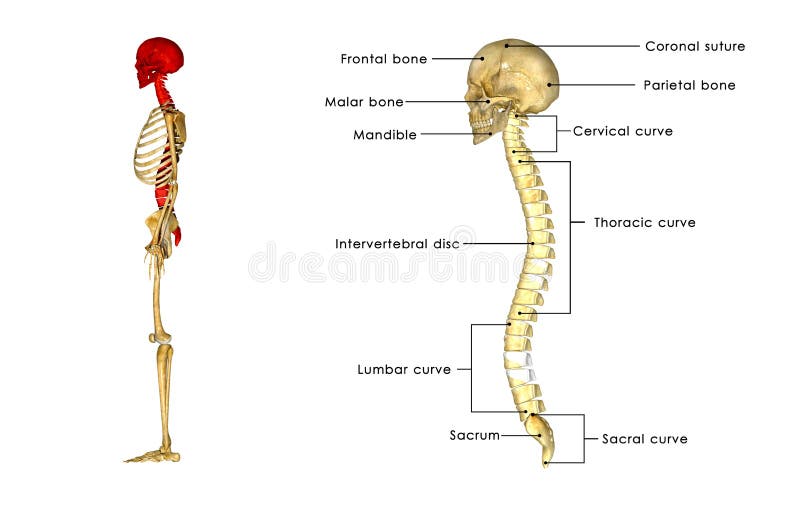



Back Bone With Skull Side View Stock Illustration Illustration Of Head Gland




Human Head Back Side Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Human Anatomy Muscle Anatomy Muscle Diagram Head Muscles
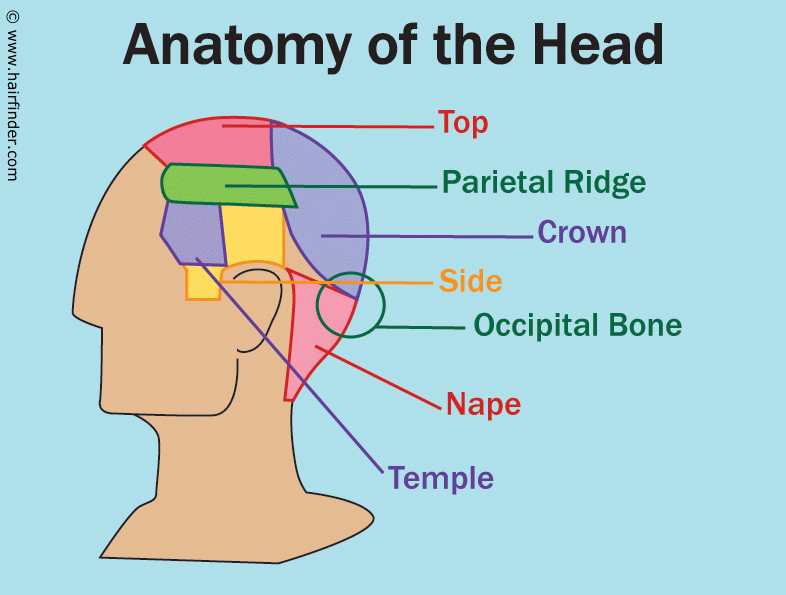



Anatomy Of The Head And The References Used For The Areas Of The Head In Haircuts And Haircutting




Temple Anatomy Wikipedia




List Of Human Anatomical Regions Wikipedia



1




Back Muscles Anatomy Of Upper Middle Lower Back Pain In Diagrams Goodpath




Head Anatomical Landmarks 35 Images Craniocerebral Topography Elements Of Morphology Human Malformation Terminology Brain Anatomy Regions And Landmarks




Xray Of Human Head Showing Neck Contortion Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Anatomical Landmarks Side And Back Views Of The Head Showing Download Scientific Diagram




Neck Anatomy Britannica




Backside Skull Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile




Skull Anatomy Terminology Dr Barry L Eppley
/my-neck-has-been-in-pain-the-whole-week-1137019824-5d735f6b63eb47c3b607993dd8b6c419.jpg)



Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Anatomy And Function
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/neurovasculature-of-head-neck/DUdNRgQUmaTFMGS6j2Y79Q_Neurovasculature_of_head___neck.png)



Nerves And Arteries Of Head And Neck Anatomy Branches Kenhub




Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Anatomical Landmarks Side And Back Views Of The Head Showing Download Scientific Diagram




Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo By C Anatomyinsider




Neck Pain On The Left Side Causes Diagnosis And Relief



Human Neck Anatomy High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Anatomy Of Back Of Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿